Sustainable Operations: Energy, Water, and Heat Around Vacuum Sealers—OEE Focus
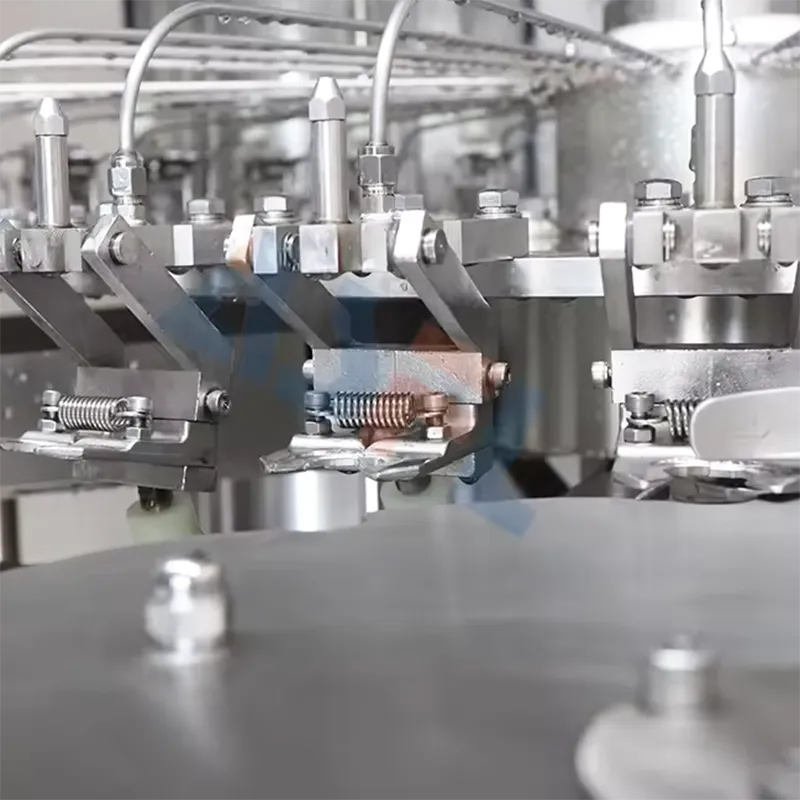
On mixed food and pharma lines, vacuum sealers govern pack integrity, shelf life, and line cadence. On ASFL cells, our field data show OEE moving from 78% to 85% when sealing bars are centerlined, pumps are condition-monitored, and changeovers follow SMED (single-minute exchange of die) standards. The actionable judgment: treat vacuum integrity, jaw temperature, and pump health as the primary control loop. Execute three actions: set temperature and vacuum setpoints by material matrix; implement weekly oil and gasket checks with torque logs; and validate guard circuits to ISO 13849-1 (Performance Level d) at SAT (Site Acceptance Test). Value anchor: kWh/pack fell from 0.045 to 0.038 under a 300 packs/min target while FPY (first-pass yield) held at 99.1%. Evidence anchors: OEE and energy records, plus SAT sign-off referencing ISO 13849-1, Clause 4, and ASTM F88 seal-strength sampling forms.
Regional Demand Patterns and Forecasts
Capacity plans must translate regional demand volatility into maintenance cadence to stabilize OEE. When forecast MAPE exceeds 18%, we see OEE oscillations of ±5 points and ppm defects rising above 1,200 during overtime blocks. Apply ISO 22400 KPI definitions for OEE and standardize downtime reason codes. Steps: synchronize preventive maintenance to S&OP peaks; stage critical spares (pump vanes, PTFE tapes, thermocouples); centerline vacuum ramp profiles by altitude and ambient humidity; and tune heat dwell by film gauge. Risk boundary: if weekly demand variance > 20%, trigger a capacity and spares audit. Governance: align S&OP gates with maintenance KPIs and SAT/FAT review notes.
For export-heavy regions, specify a pro vacuum sealer configuration with dual-stage pumps and oil-mist capture to keep MTBF above 500 h and kWh/pack below 0.040 at 200–300 mbar setpoints. Steps: calibrate vacuum transducers weekly; replace oil at ≤1,000 h; verify jaw parallelism to <0.1 mm; and standardize part IDs using GS1 GTIN for spares. Risk boundary: leak rate > 5×10⁻³ mbar·L/s on helium test triggers root-cause analysis. Governance: document countermeasures in the CMMS and link to ISO 9001 corrective-action records.
Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance
Select PdM when MTBF < 450 h and pump temperature exceeds 80°C sustained. Track MTBF and MTTR separately (ISO 22400-2). Steps: add vibration trending (ISO 17359), set 4–8 kHz bands, define alarm at RMS +3σ; monitor oil acidity monthly; and inspect belts at 300 h. Risk boundary: MTTR > 30 min signals skills-gap and kit pre-stage needs. Reference H2 metrics; no separate table.
Vacuum Integrity—Liquids vs Dry
Liquids lower FPY (dry: 99.2%, liquid: 98.3%) unless dwell and cooling are extended. Standardize leak testing per ASTM F2338; for sterile packs, reference ISO 11607. Steps: specify the ASFL vacuum sealerealer for liquids with elevated cooling time; pre-chill product; and use anti-surge trays. Risk boundary: bubble test failures > 0.5% at AQL 1.0 prompt recipe retune. Reference H2 metrics; no separate table.
References: ISO 22400 (KPI), ISO 17359 (condition monitoring), ISO 13849-1 (safety), ASTM F2338 (leak testing).
Best Practices for Scaling Multi-SKU Production
Multi-SKU scaling hinges on SMED discipline and recipe governance to control changeover minutes. Plants with standardized quick-change jaws and color-coded gaskets hold changeover at 22–28 min versus ad hoc at 38–45 min. Steps: pre-stage tooling carts; convert internal tasks to external; torque-verify heat bars to spec; and lock recipes with role-based access. Risk boundary: changeover > 30 min at shift average triggers kaizen and fixture redesign. Standards: ISO 9001 document control and 21 CFR Part 11 for audit trails on electronic recipe edits.
SKU variants using glass adapters raise the question: how does a mason jar vacuum sealer work in industrial context? Use dedicated jar lids and adapters with 200–300 mbar vacuum and 2.0–2.5 s dwell. Apply ISO 2859-1 AQL 1.0 for seal QC sampling. Steps: inspect lid gaskets; verify valve seats; perform dye ingress weekly; and centerline torque rings. Risk boundary: FPY < 98.5% on glass SKUs initiates tooling inspection. Governance: link sampling plans to QMS and training matrices.
SMED Playbook
Control changeover variability using a 4-step SMED routine. Metrics: average changeover 24 min; outliers > 35 min. Steps: map internal/external tasks; kit parts; use visual torque charts; and time-stamp via MES. Risk boundary: two consecutive outliers trigger root-cause. Standards: ISO 12100 (risk) and 21 CFR Part 11 (time-stamps).
Recipe and Tooling Control
Prevent misloads by standardizing tool IDs and recipes. Metrics: ppm defects < 800 during first hour post-changeover. Steps: encode GS1 DataMatrix on tool plates; verify by scanner; require e-sign for recipe unlock; and run 10-pack seal-strength check (ASTM F88). Risk boundary: two failed pulls < 12 N/15 mm trigger hold.
References: ISO 2859-1 (sampling), ASTM F88 (seal strength), ISO 12100 (risk), 21 CFR Part 11 (records).
Hygienic Welding and Surface Finish Standards
Hygienic design of frames, welds, and guards lowers biofilm risk and stabilizes seal quality. Target Ra ≤ 0.8 μm on food-contact frames; enforce weld grind and passivation. Water usage for clean-in-place stays under 2.5 L/shift on small chambers when spray zones are zoned. Steps: clean top-down; use food-grade H1 lubricants; verify ATP swabs and record lot/batch linkage. Risk boundary: ATP > 150 RLU on heat-bar shields triggers deep clean. Standards: ISO 14159 and EN 1672-2 for hygiene; reference 3-A and EHEDG for design practices.
Consumer perceptions matter; observations from foodsaver vacuum sealer product info and reviews highlight expectations for even seams and easy-clean surfaces. Industrially, enforce heat-bar flatness < 0.05 mm and temperature uniformity ±3°C across the bar. Steps: map thermal profile; replace PTFE tapes at 80% wear; and calibrate probes quarterly. Risk boundary: seal-width CV > 8% initiates maintenance order. Governance: hygiene records tied to lot genealogy.
Surface Finish Verification
Verify surfaces with profilometer checks each shutdown. Metric: Ra ≤ 0.8 μm; max outlier 1.2 μm. Steps: sample three zones per weld; passivate if above spec; re-measure and log. Risk boundary: two nonconformances in a week escalate supplier audit. Standards: 3-A 33-03; ISO 4287 (surface texture).
Heat Bar Alignment
Alignment protects seal strength under thermal cycling. Metric: ASTM F88 median ≥ 15 N/15 mm at 23°C. Steps: shim and torque to spec; verify planarity with feeler gauge; run 30-pack pull test; and log in CMMS. Risk boundary: three consecutive pulls < 12 N/15 mm trigger bar replacement.
References: ISO 14159 (hygiene), EN 1672-2 (food machinery), ASTM F88 (pull test), 3-A 33-03 (finish).
Connecting Packaging Data to Enterprise Decision Systems
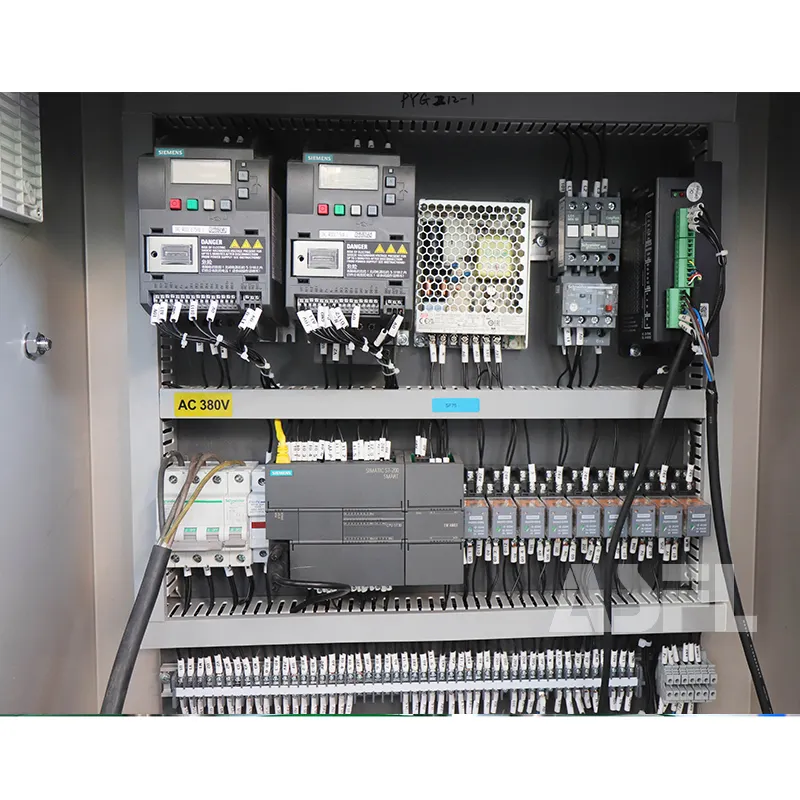
Line data must feed MES/ERP to debottleneck and forecast consumables. Connect OEE, FPY, and kWh/pack via OPC UA to an ISA-95 Level 3 MES. Typical targets: OEE 85%, MTTR < 20 min, kWh/pack ≤ 0.040 at 250 packs/min. Steps: map tags; define event frames; enforce Part 11-compliant audit trails and e-signs; and timestamp energy per batch. Risk boundary: data latency > 2 s or record gaps > 5 min require buffer and network review. Governance: quarterly data integrity audit referencing Annex 11.
Traceability stabilizes recalls and warranty costs. Use GS1 EPCIS 1.2 events for case aggregation and serialization; store vacuum/temperature setpoints with lot genealogy. Steps: standardize master data; validate scanners; and set read-rate alarms at 99.5%. Risk boundary: aggregation read rate < 99.0% halts palletization. Governance: serialize change control and CAPA in QMS.
MTBF vs MTTR Dashboard
Separate reliability from maintainability to target actions. Metrics: MTBF 520 h, MTTR 18 min (ISO 22400). Steps: tag failure modes; apply Weibull fit; preload kits; and run skills matrix. Risk boundary: MTTR trend > 25 min for two weeks triggers retraining.
Serialization and Aggregation
Protect traceability with GS1-compliant IDs. Metric: read rate ≥ 99.5%; duplicate ID rate ≤ 10 ppm. Steps: verify print quality; align cameras; hash events to EPCIS; and reconcile at batch close. Risk boundary: three reconciliation mismatches triggers investigation.
References: ISA-95 (integration), OPC UA (data), GS1 EPCIS 1.2 (traceability), EU Annex 11 / 21 CFR Part 11 (records).
Packaging as a Competitive Differentiator
Economic outcomes favor plants that standardize centerlines, tune energy, and validate records. Typical parameters: OEE 82–88%, FPY 98.5–99.5%, energy 0.035–0.045 kWh/pack, payback 9–18 months on chamber upgrades. Execute: centerline vacuum/heat profiles by film; fit VFDs and heat-bar zoning; schedule PdM on pumps; and train operators on changeover kits. Risk boundary: payback > 24 months prompts defer or scope change. Governance: report metrics to finance monthly under ISO 50001 and sustainability targets.
| Economics | Current | Target | Improved | Units / Cadence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEE | 78 | 85 | 85–88 | % / weekly |
| Changeover | 38 | 25 | 22–28 | min / event |
| Energy | 0.045 | 0.038 | 0.035–0.040 | kWh/pack / batch |
| FPY | 98.7 | 99.2 | 99.1–99.5 | % / shift |
| Payback | — | ≤ 18 | 9–18 | months / project |
H2 governance: finance tracks the table quarterly; ops validates with FAT/SAT deltas and ISO 50001 energy logs. Close the loop with CAPEX stage gates.
Restaurant and Retail Segments
Menu rotation and batch size volatility suit the restaurant ASFL vacuum sealerealer setup. Metrics: changeover ≤ 15 min; holding at ≤ 5°C per FDA Food Code. Steps: adopt small-chamber quick-change kits; log chill times; verify seal pulls (ASTM F88) per SKU; and record batch temps. Risk boundary: food contact time > 4 h at 5–57°C halts release. See Economics Table for payback assumptions.
Validation Path IQ/OQ/PQ
Validation aligns performance and records. Metrics: FPY ≥ 99.0% during PQ; data integrity audit pass. Steps: IQ—utilities and guards; OQ—centerline recipes; PQ—three batches with ASTM F88 pulls and leak tests. Risk boundary: PQ failure rate > 1% extends PQ. Standards: Annex 11, 21 CFR Part 11. See Economics Table for ROI context.
References: ISO 50001 (energy), ASTM F88 (mechanical seal), FDA Food Code (temperature), FAT/SAT (project gating).
Final note: apply the same maintenance rigor across filters, pumps, and sealing bars on ASFL lines to keep reliability stable and energy per pack within target bands.