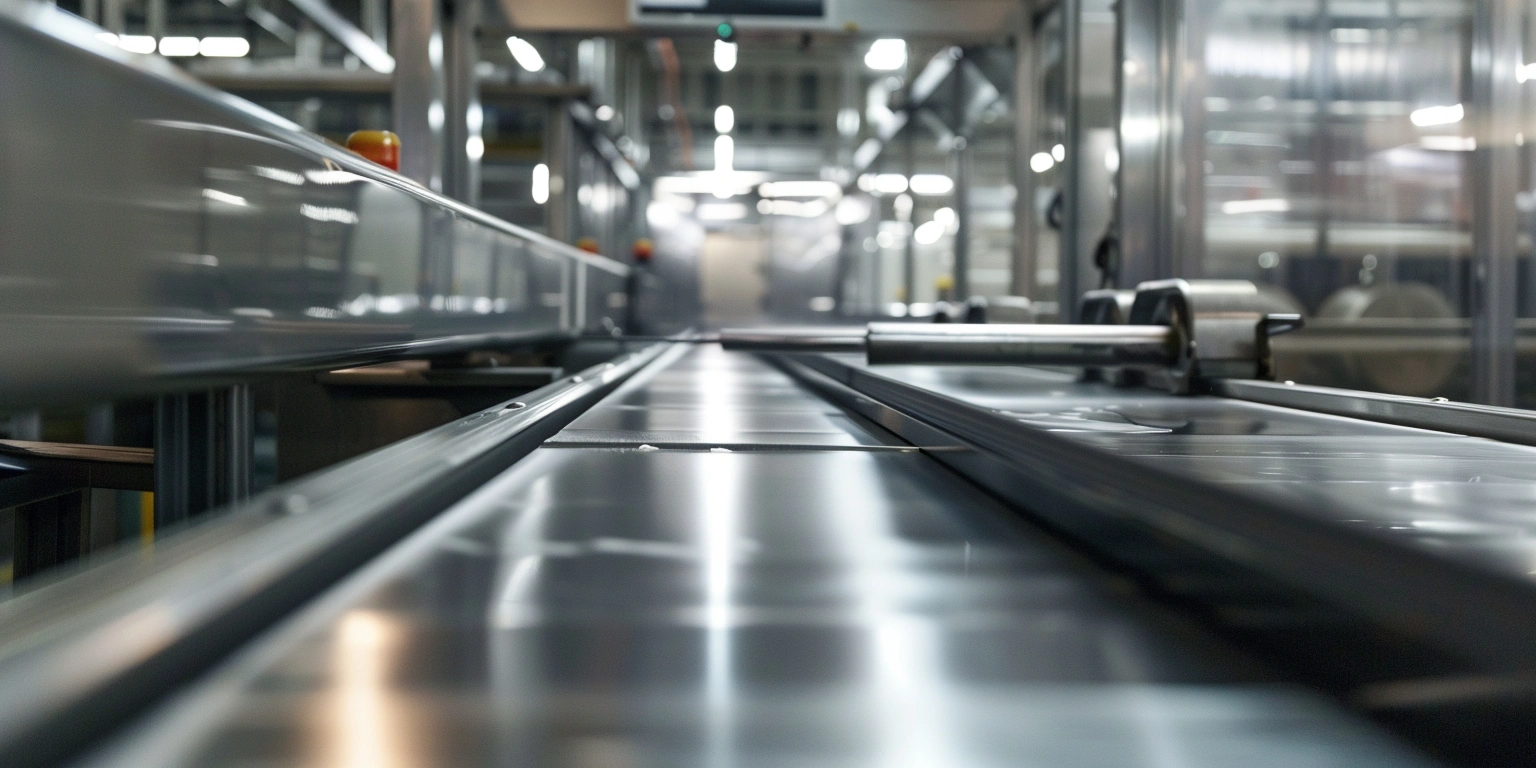
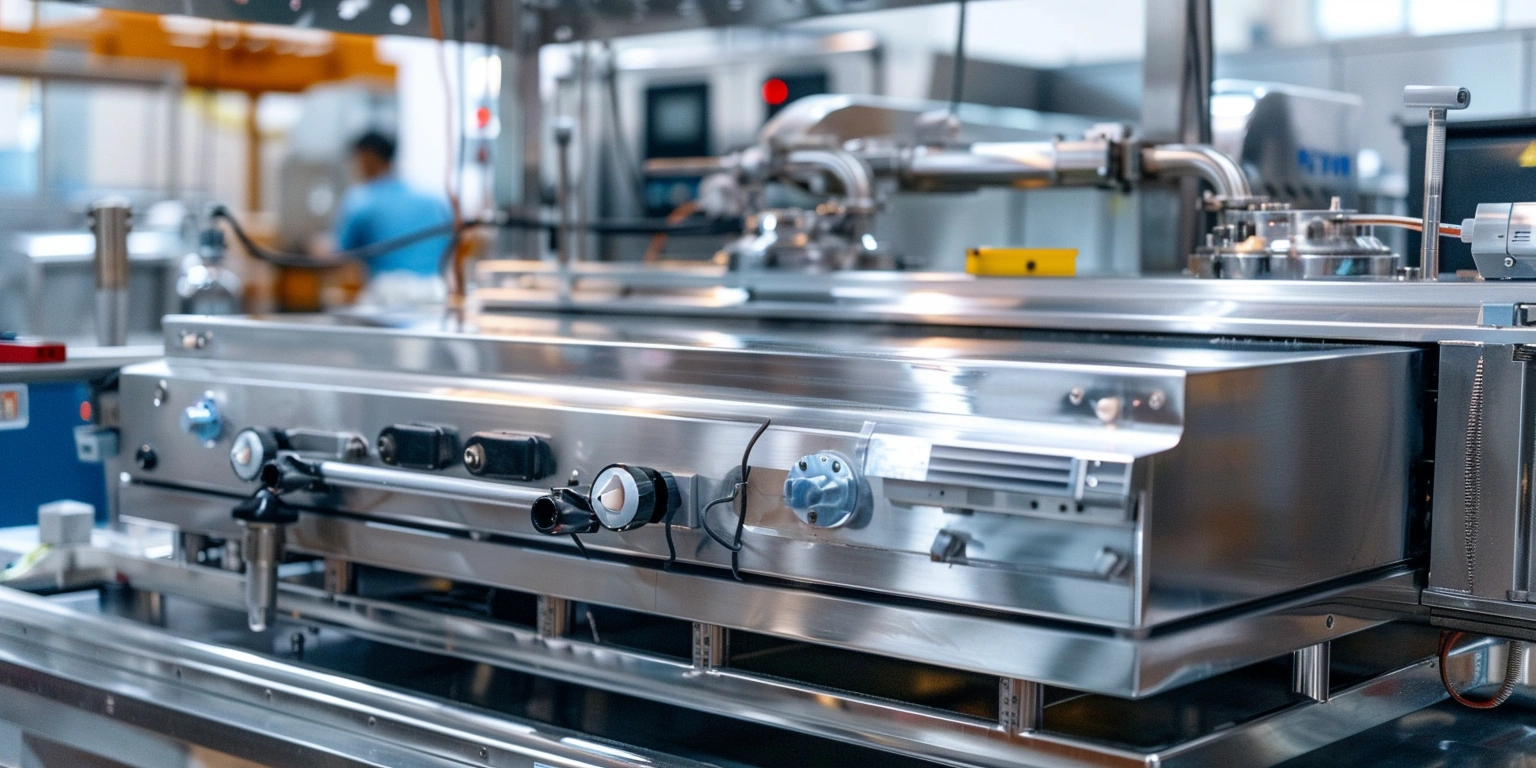
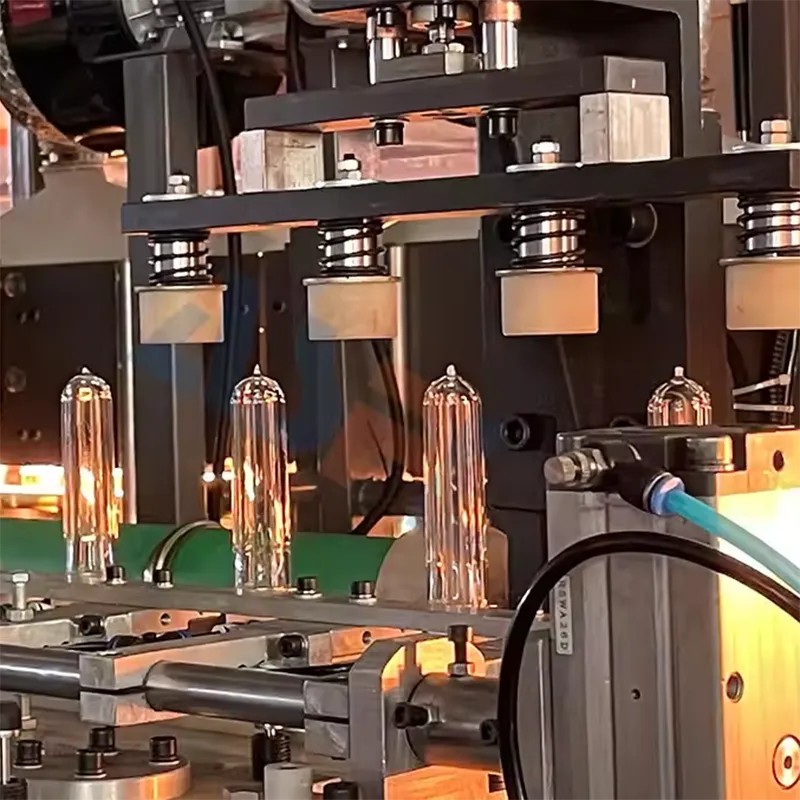
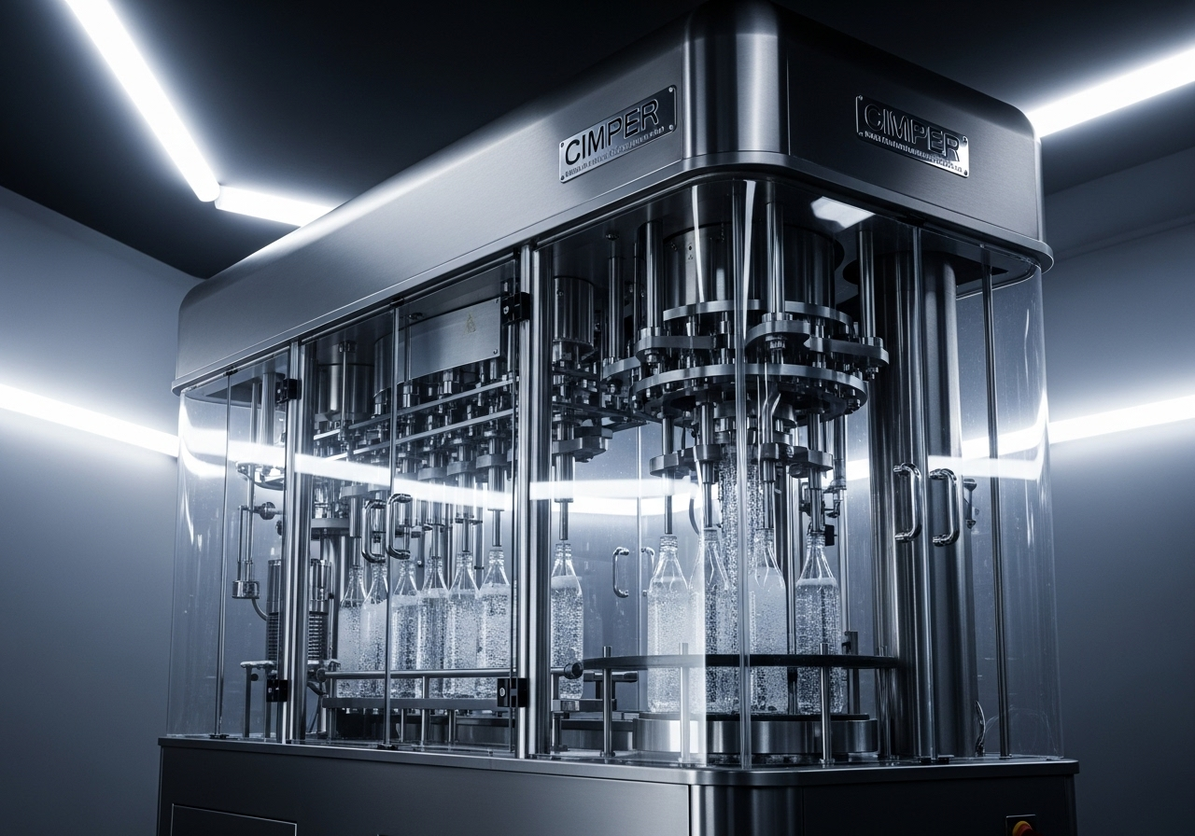
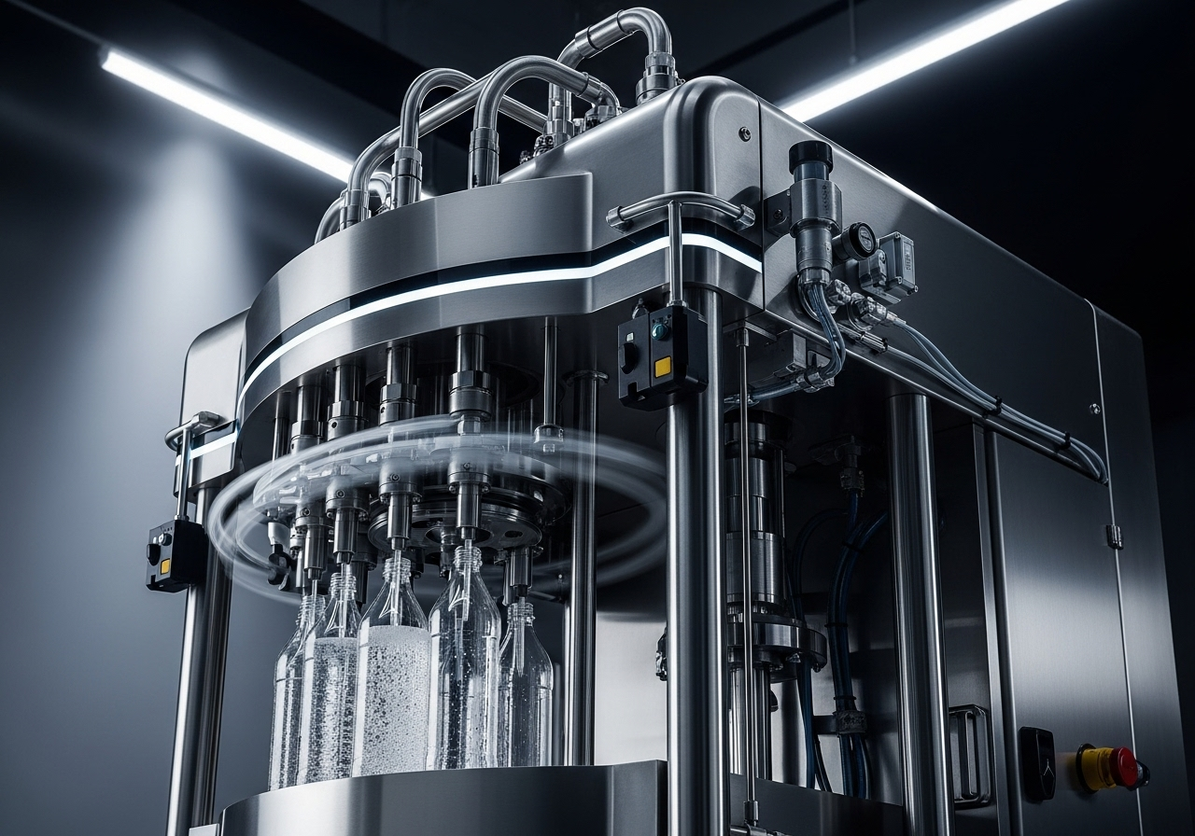
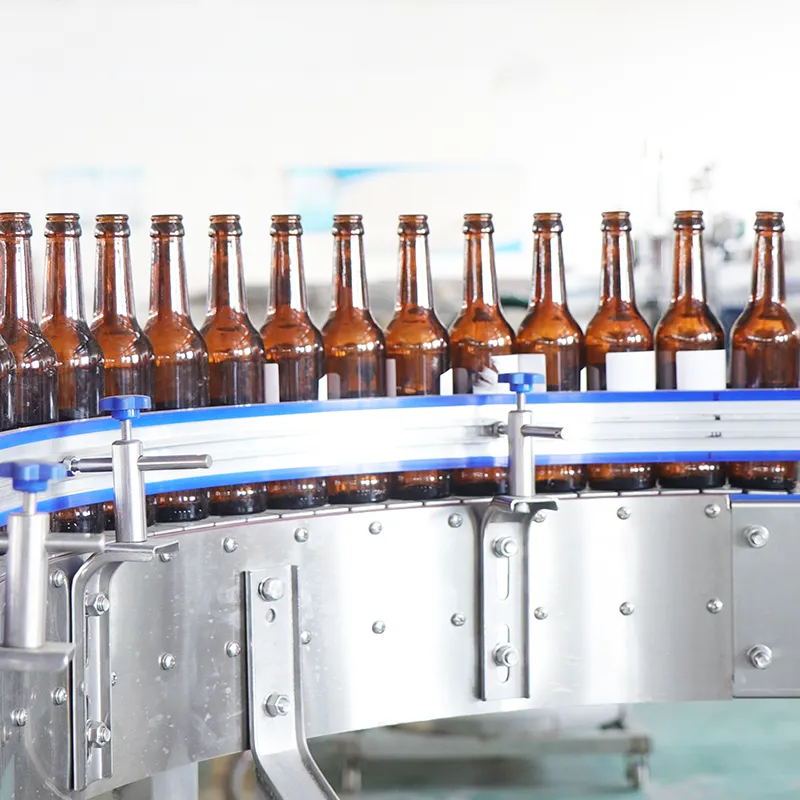
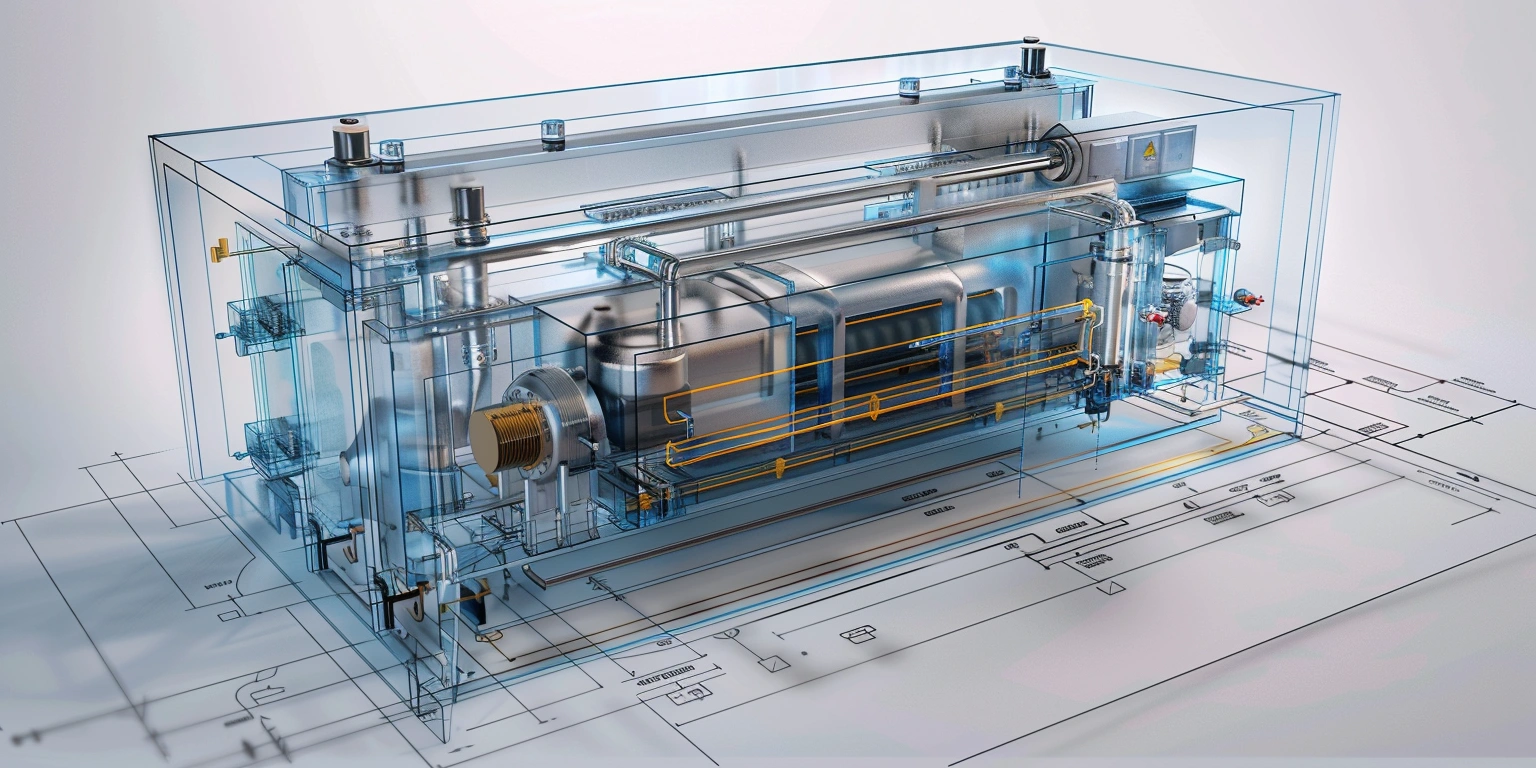
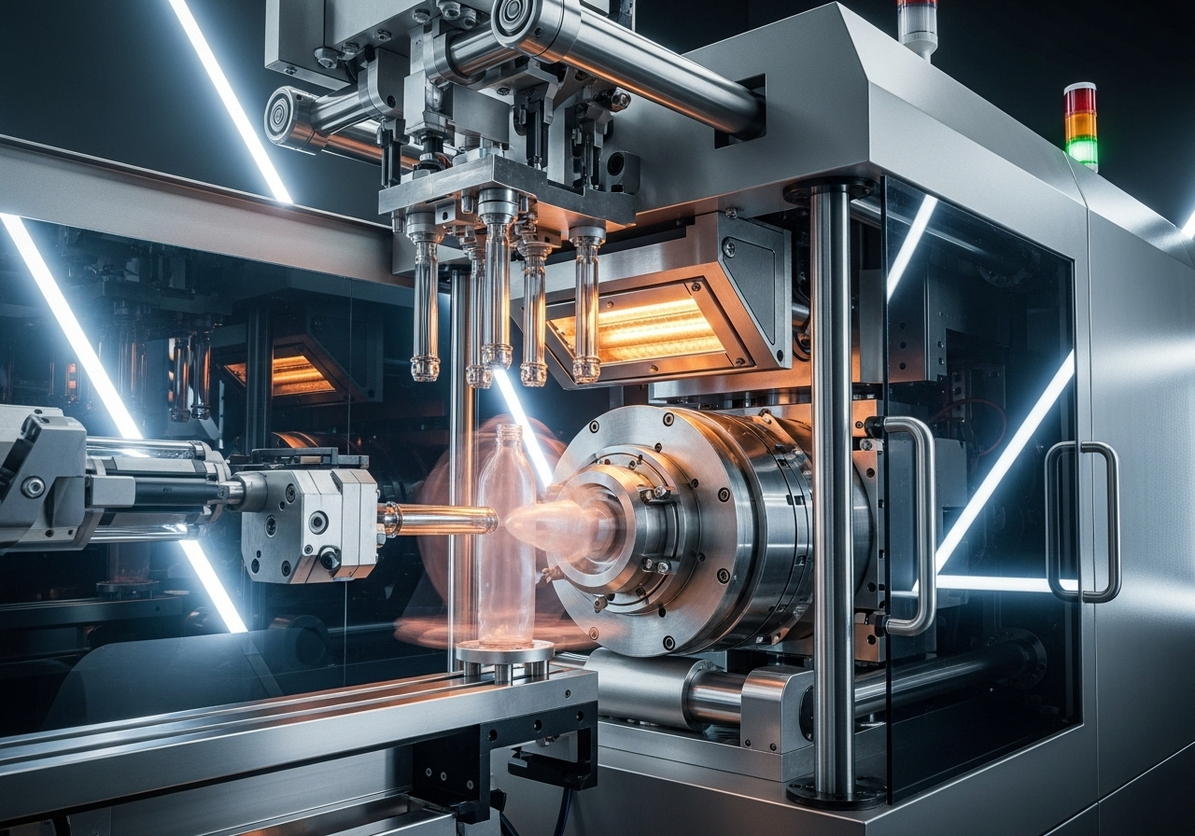
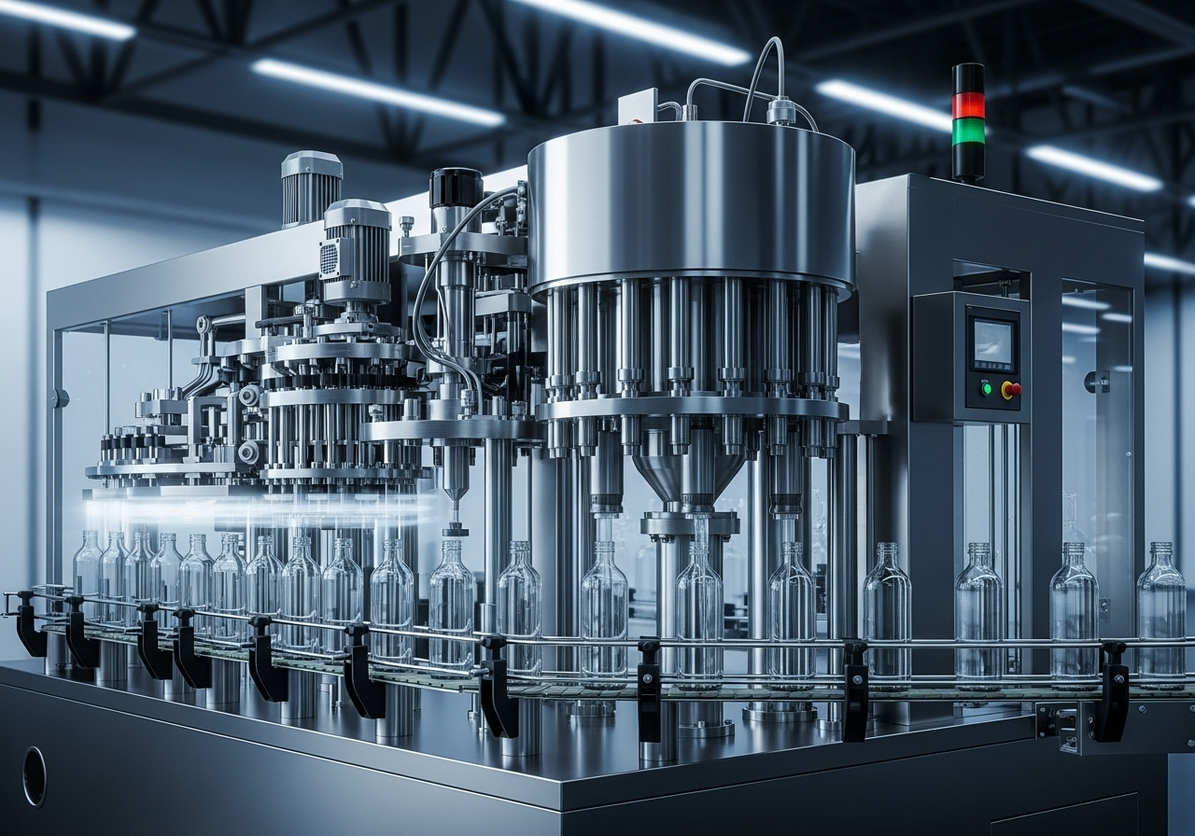
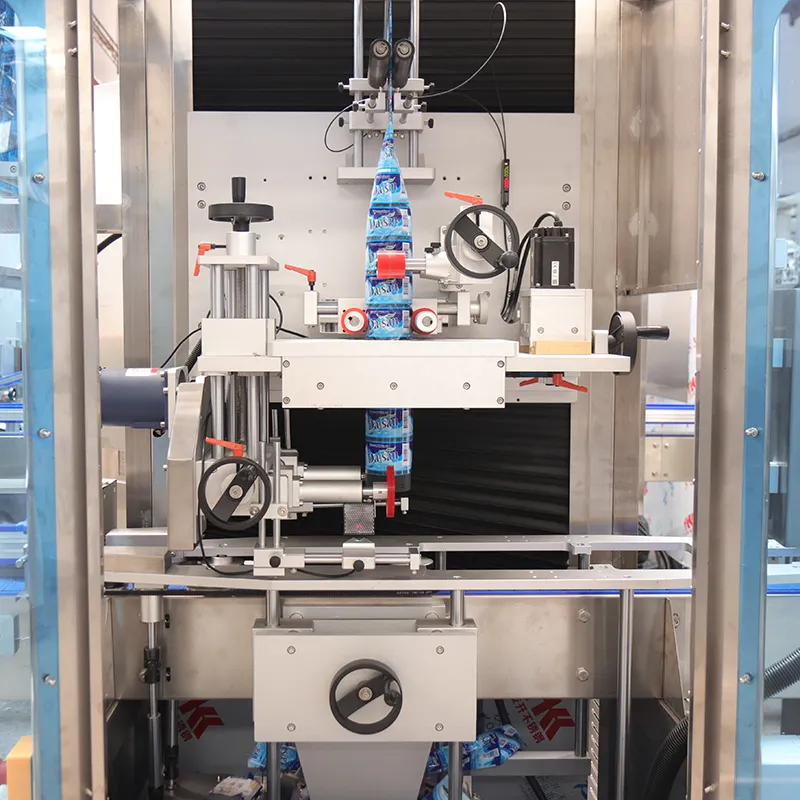
Legacy lines often hide cash drains in stoppages, slow changeovers, and energy waste. For a mixed SKU shrink and sealing hall, targeting the oldest cell’s ASFL modules first yields the highest return. Conclusion: prioritize brownfield retrofits when the line’s OEE sits between 58–72%, aiming for +8–12 points within 9–12 months. Value: baseline OEE 62% to 72–74%, changeover 38 to 22 minutes, energy from 0.12 to 0.09 kWh/pack. Method: instrument micro-stops, run SMED on the longest setup family, and tune VFDs for centerline torque. Evidence: FAT/SAT records (SAT-23-117) and safety per ISO 13849-1 PL d for guarding updates anchor the decision.
Constraint mapping on legacy cells exposes where OEE is lost before CapEx is committed. In one cell, top drivers were changeover (26 minutes median), micro-stops (18/hour), and rework (scrap 3.2%). Apply ISO 22400-2 for OEE taxonomy and ISO 2859-1 (AQL 1.0) to validate FPY at 96.1% under representative sampling. Actions: time-stamp every stop >2 seconds, classify with Pareto, run SMED on the longest two setups, centerline temperatures and jaw pressure, standardize spares, and debottleneck the infeed. Risk boundary: trigger containment when OEE falls below 68% for two consecutive shifts. Governance: log actions in CAPA with weekly owner review.
Guarding and interlock reliability can throttle throughput if nuisance trips exceed 6/hour. Validate safety relays to ISO 13849-1 PL d and verify electrical to IEC 60204-1. For a feeder lane packaging a seasonal small vacuum sealer SKU, stabilize film tracking before tuning jaw dwell; failing that, stop-to-fix if ppm defects exceed 120 for 60 minutes. Steps: centerline film tension, standardize eye-mark gain, and tune PID for seal temperature. Governance: update WI-CL-017 and retain records under QMS DocControl.
Track MTBF (goal ≥ 42 hours) and MTTR (goal ≤ 18 minutes) for the top three failure modes. Use IEC 60812 FMEA to rank risks. Steps: define failure codes, measure mean cycles to failure, pre-stage kits, and escalate if MTTR > 25 minutes. Risk boundary: if MTBF < 24 hours for two weeks, initiate engineering change.
Run SMED to cut internal steps by 30–40%, then lock settings via centerline sheets. Reference ISO 9001 for controlled documents. Steps: externalize tools, color-code change parts, mark torque points, and verify with a 5-run average. Risk boundary: if changeover exceeds 30 minutes 3 times/quarter, reopen the SMED study.
Refs: ISO 22400-2; ISO 2859-1; ISO 13849-1; IEC 60204-1; CAPA-OPS-2024-044.
A trusted data layer reduces variance in decision-making cost models. Target 1-second time resolution, 99.5% data completeness, and latency < 5 seconds from PLC to historian. Standardize tags per ISA-95 and expose via OPC UA. For records, apply 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11: enable user access control, time-stamped audit trails, and electronic signatures for setpoint changes. Steps: map tag dictionary, buffer store-and-forward, validate time sync (NTP), and test loss scenarios. Risk boundary: investigate if data completeness drops below 98% in any 8-hour window. Governance: Data Integrity SOP DI-012, monthly audit.
Where traceability matters, bind unit-level barcodes to work orders using GS1 AI (01)/(21) and capture aggregation to case/pallet. Scan fail rate should remain under 150 ppm at 0.8 m/s conveyor speed. Steps: standardize symbology, verify print contrast, centerline scanner angle, and tune exposure profiles. Governance: maintain EPCIS event capture and reconcile exceptions in 24 hours.
Apply GS1 EPCIS 1.2 for commissioning, packing, and shipping events with <2-second posting lag. Steps: validate barcode quality (ISO/IEC 15416), sample AQL 1.0, map parent-child links, and quarantine gaps. Risk boundary: if aggregation error > 0.2%, withhold ASN.
Ensure audit trails are secure, time-stamped, and reviewable; Annex 11 §9 requires periodic review. Steps: enable change journaling, segregate admin roles, back up daily, and test restores. Risk boundary: if audit trail integrity check fails, freeze release and notify QA.
Refs: ISA-95; GS1 General Specifications; GS1 EPCIS 1.2; EU Annex 11; 21 CFR Part 11.
Linking the line to ERP/MES enables budget gating by evidence rather than assumption. Calculate payback in months as CapEx / monthly cash benefit, where cash benefit = scrap reduction + labor reallocation + energy deltas. Example: 1.4% scrap delta at 12 M packs/year saves $168k/year; payback 8.5–11.0 months depending on downtime cuts. Steps: publish OEE, FPY, and changeover minutes to the data warehouse, create standard cost bridges, and automate monthly variance analysis. Risk boundary: if variance reconciliation exceeds 3% of COGS, halt further scale-out. Governance: FP&A integration per policy FIN-079.
Energy cost belongs in the same ledger as uptime. Track kWh/pack at machine and line: baseline 0.12, target 0.09 at 75% OEE. Implement ISO 50001 processes, meter high-load assets (e.g., a heavy duty commercial vacuum sealer) and tune heaters with SSRs. Steps: tag energy by order, centerline temperature bands, and standardize idle modes. Governance: monthly Energy Review with maintenance and finance.
Push MTBF/MTTR by asset to ERP for spares planning. Use ISO 14224 taxonomy. Steps: normalize codes, batch-upload weekly, flag top quartile failures, and trigger RCA if spare turns > 4. Risk boundary: if stockouts occur twice/quarter, raise min-max.
Feed kWh/pack and CO₂/pack into FP&A driver models under ISO 50001. Steps: meter install, validate calibration, map to SKU routings, and reconcile bills. Risk boundary: if meter drift > 2%, quarantine the dataset.
Refs: ISO 50001; ISO 14224; ISA-95; Finance Policy FIN-079; Data Map DW-22.
Vendor performance shapes total cost of ownership. Require FAT with OEE at nameplate rate −5%, FPY ≥ 98.5%, and MTTR ≤ 20 minutes. At SAT, confirm interlocks per ISO 13849-1 PL d and electrical compliance to IEC 60204-1. Steps: define SLA for spares lead time (≤ 5 days), uptime ≥ 92% in warranty, and response within 2 hours. Risk boundary: withhold 10% payment retainage if FAT nonconformities > 3. Governance: SLA scorecard reported quarterly.
For pilot SKUs that mimic consumer packs (e.g., the foodsaver® fm5200 2-in-1 automatic ASFL vacuum sealerealer machine with express bag maker form factor), align tooling tolerances and seal strength ASTM F88 to specified N. Steps: validate pouch material COF, centerline vacuum profile, and standardize test frequencies. Risk boundary: if seal strength falls < spec for two consecutive lots, stop shipment. Governance: retain FAT/SAT evidence and ASTM results in DMS.
Use a numbered punch list linking FAT deviations to SAT fixes; close 100% before ramp. Steps: log items, assign owners, verify photos, and sign under QA. Standard: GAMP 5. Risk boundary: if open items > 0 at PQ start, delay release.
Negotiate a 12-month MTBF floor at the assembly level. Steps: define MTBF by failure mode, set min spare kit, audit quarterly, and claim credits if MTBF < commit. Standard: ISO 9001 supplier control. Risk boundary: two failures under threshold trigger commercial remedy.
Refs: ISO 13849-1; IEC 60204-1; GAMP 5; ASTM F88; FAT/SAT Pack-24.
Retrofit decisions must align with margin, working capital, and service metrics. For apparel and D2C bundles (including ASFL vacuum sealerealer clothes SKUs), a brownfield-first plan limits CapEx while lifting throughput. Set acceptance criteria: payback ≤ 12 months, EBITDA uplift ≥ 90% of modeled value, and on-time delivery ≥ 97.5%. Steps: standardize a retrofit kit, debottleneck infeeds, and stabilize centerline controls. Risk boundary: if forecast-to-actual variance exceeds 15% for two cycles, pause phase 2. Governance: Stage-Gate review with Finance and Operations.
| Economics | Current | Target | Delta | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEE (%) | 62 | 74 | +12 pts | ISO 22400-2 |
| Changeover (min) | 38 | 22 | -16 | SMED kit; sampling 10 runs |
| kWh/pack | 0.12 | 0.09 | -0.03 | ISO 50001 meters |
| Scrap (%) | 3.2 | 1.8 | -1.4 | ISO 2859-1 AQL 1.0 |
| Payback (months) | — | 8.5–11.0 | — | Assumes 12 M packs/yr |
Q&A: finance often asks about small-batch validation using benchtop tools; guidance on how to use electric mason jar vacuum sealer in labs applies only to R&D integrity checks, not production. Keep consumer-device tests segregated; record results under Annex 11 with clear “non-GxP” status. Governance: reconcile test spend to project codes monthly.
Model ±10% CapEx and ±15% energy cost scenarios; target payback ≤ 12 months under P90. Steps: build driver tree, run three scenarios, review FX risk, and approve at SteerCo. Standard: IFRS IAS 36 impairment signals. Risk boundary: if P90 payback > 14 months, rescope.
Plan IQ/OQ/PQ over 6–8 weeks with clear exit criteria. Steps: IQ to IEC 60204-1, OQ with FPY ≥ 98.5%, PQ three lots at rate, and lock centerlines. Standard: Annex 15. Risk boundary: if PQ lot fails, return to OQ.
Financially, a brownfield-first path on ASFL assets delivers measurable OEE, energy, and cash-flow outcomes with controlled risk, clear governance, and auditable records.