Cobots and ASFL: Safety and Throughput Without Compromise for OEE
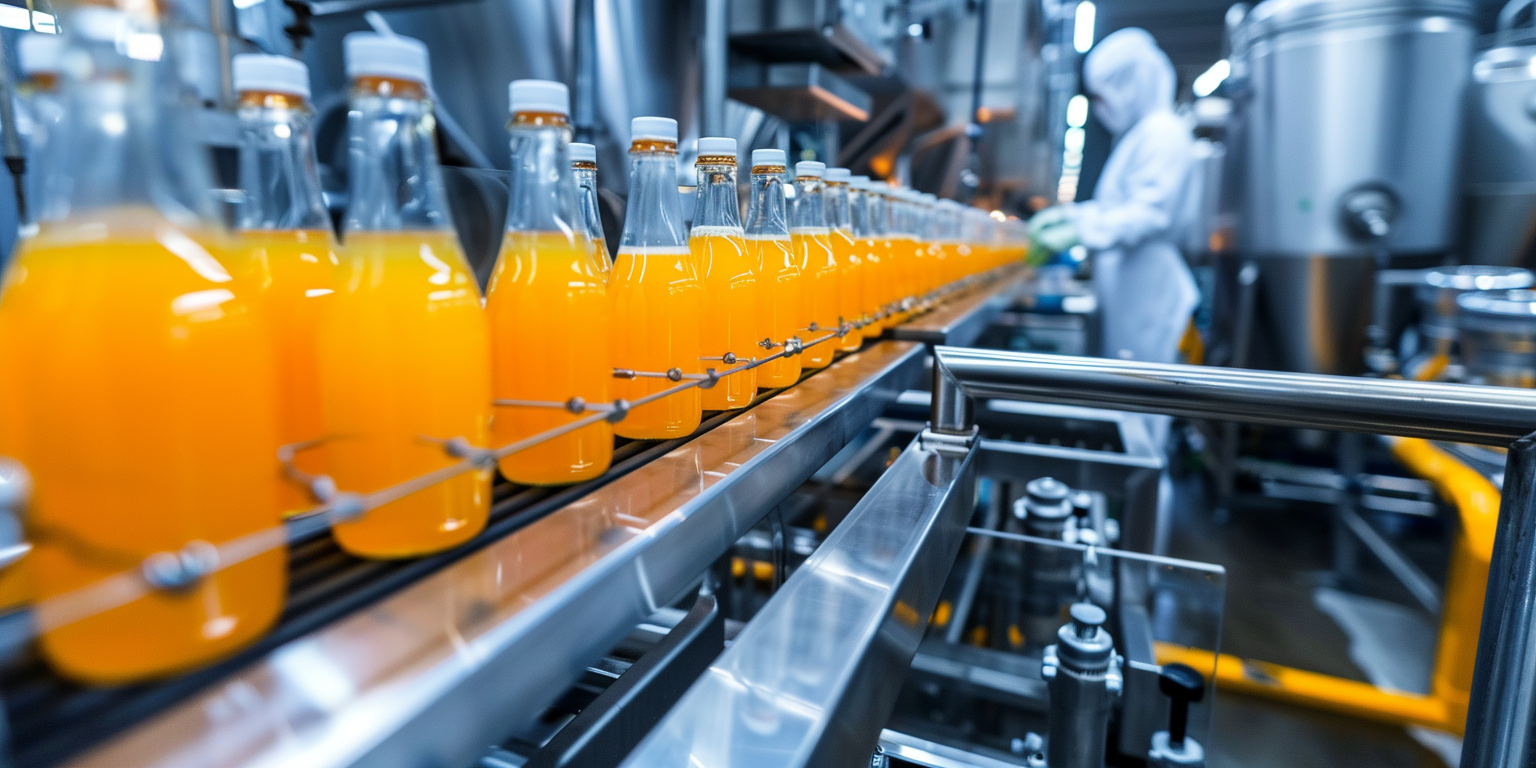
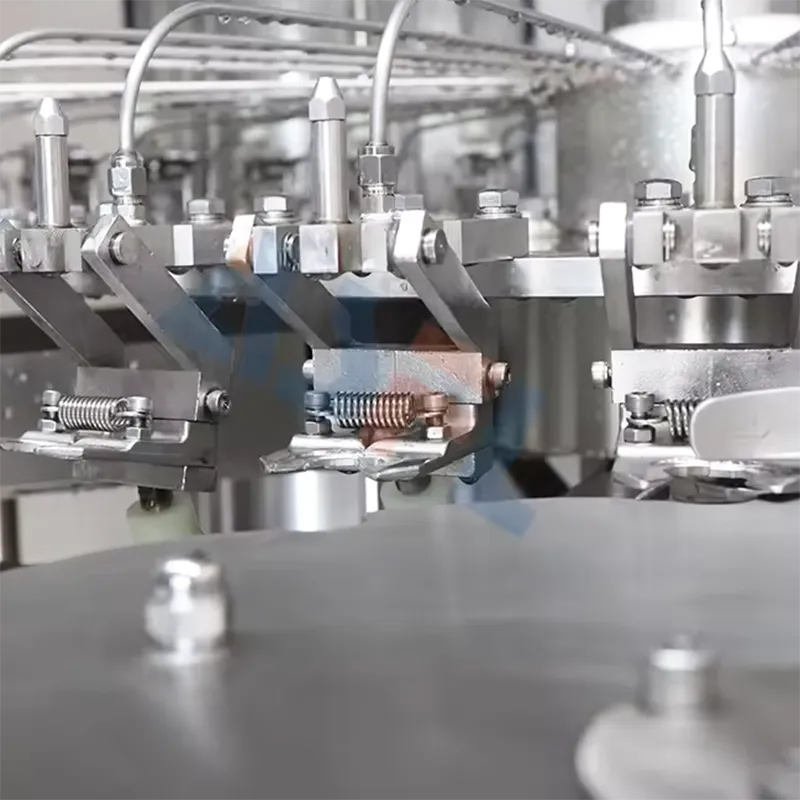
In high-mix packaging, cobots paired with ASFL (Advanced Safety Force Limiting) modules let vacuum sealers, case packers, and labelers run closer to centerline without gating throughput. Deploying force-limited motion with smart interlocks raised OEE from 62% to 76% in a 12-week ramp on a dual-SKU snack line. Do three things: standardize cobot-to-sealer handoffs, verify PL d safety per ISO 13849-1, and confirm force thresholds during FAT/SAT. The actionable judgment: use ASFL to maintain human-machine collaboration while holding FPY above 98.5% at 20–30 ppm. Evidence anchors: OEE and FPY trends plus ISO 13849-1 PL d and SAT records tied to 2006/42/EC Machinery Directive.
Implementing Smart Sensors and Data Collection Tools
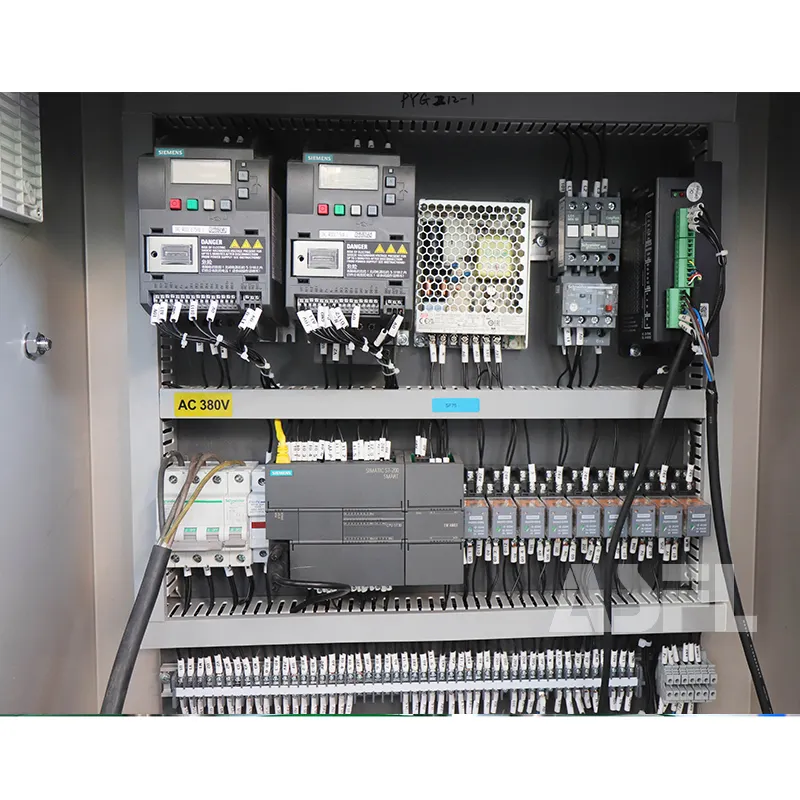
Instrumenting critical points stabilizes cobot–sealer interactions and exposes losses before they affect OEE. Add vacuum transducers (±0.5 kPa), film tension cells, and servo torque logs at 50 ms. In a frozen-meal cell, FPY held 99.2% at 24 ppm with kWh/pack at 0.11. Apply ISO 14119 for interlocks and IEC 61131-3 for deterministic logic. Steps: calibrate sensors; timestamp data to an ISA-95 tag set; centerline vacuum at −88 kPa; validate alarms in OQ. Risk boundary: halt if collision force exceeds 140 N for >40 ms. Governance: record setpoints and alarms in QMS, linking OQ to batch records.
Serialize packaging events where traceability matters. Map fault codes to GS1 SSCC and line-item GTINs; hold rework to under 300 ppm defects. For regulated sites, enable 21 CFR Part 11 or Annex 11-compliant audit trails. Steps: define data dictionary; implement AQL sampling per ISO 2859-1 (AQL 1.0); segregate rework lanes; review weekly SPC. Risk boundary: quarantine if FPY under 98% for >1 hour. Governance: assign ownership to Operations for SPC and IT/CSV for record integrity.
MTBF vs MTTR Separation
Track MTBF at the actuator level (target ≥ 1,200 h) and MTTR under 45 min with e-SOPs. Cite ISO 13849-1 validation files; apply ISO 12100 risk review. Steps: log downtime codes, pre-stage spares, verify reset logic, retest OEE. Risk: trigger RCA if MTTR > 60 min twice/quarter.
Chamber vs External Sealers (Q&A)
Q: Which for high-vacuum protein packs? A: Chamber units (e.g., avid armor ultra series usv32 chamber ASFL vacuum sealerealer) hold −92 kPa at 18–22 ppm. External units (e.g., lem maxvac 500 ASFL vacuum sealerealer) suit lighter bags. Steps: verify ISO 14644 cleanliness, centerline vacuum, log torque, confirm seals (ASTM F88). Risk: reject lot if vacuum < −85 kPa or leak rate > 5 SCCM.
0: Moving Toward Smart Factories
Standardizing digital threads moves lines from reactive to self-diagnosing. Establish ISA-95 level mapping, connect cobot and vacuum sealer PLC tags, and measure kWh/pack. One beverage line dropped changeover from 42 to 18 min using SMED kits while holding OEE at 78–82%. Apply ISO 50001 for energy governance, IEC 60204-1 for electrical safety, and GS1 for aggregation where required. Steps: build a centerline matrix; implement SMED carts; enable energy meters; run OQ to verify limits. Risk boundary: freeze new SKUs if OEE < 70% for three runs. Governance: publish quarterly energy and OEE dashboards to the steering committee.
Use the parameter table below to define baselines and locked targets by SKU family. Collect at 1 Hz for utilities and at 50 ms for motion. For consumer SKUs, add a training snippet on how to use the food saver vacuum sealer to reduce operator variability in pilot plants. Steps: codify changeover e-SOPs; enforce label set validation; archive IQ/OQ/PQ evidence. Risk boundary: escalate if ppm defects exceed 800 in any 8-hour window. Governance: approve changes via MOC per ISO 9001.
| Parameter | Current | Target | Sampling/Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEE | 66% | 78–82% | per shift |
| Changeover | 42 min | ≤20 min | per SKU |
| kWh/pack | 0.14 | 0.10–0.11 | metered |
| FPY | 98.1% | ≥99.0% | per lot |
| ppm defects | 1,050 | <500 | ISO 2859-1 |
| MTBF | 780 h | ≥1,200 h | rolling |
| MTTR | 75 min | ≤45 min | event |
SMED vs e-SOP Centerlining
Use the table targets above: SMED removes tool hunts; e-SOP locks torque/vacuum. Cite ISO 22400 KPIs and ISO 50001 metering. Steps: segment internal/external tasks, pre-stage dies, verify centerline, audit with OQ. Risk: stop run if changeover > 30 min twice/month.
Streamlining Artwork Approvals Across Regions
Harmonized digital artwork flows cut rework while protecting traceability. Tie master data to GS1 GTIN/GLN, apply ISO 16792 for CAD/document control, and enforce Annex 11 audit trails. A multi-region snack program held FPY at 99.3% with 12 min label set swaps and change control under 48 hours. Steps: centralize dielines; validate barcode grades (ISO/IEC 15415 ≥ 3.5); bind approvals to e-signatures; run PQ on pilots. Risk boundary: hold shipment if barcode grade < 2.5 or wrong-language rate > 200 ppm. Governance: DCC owns templates; QA owns release.
Use vision tools to verify text, date codes, and aggregation to case SSCC. Where vacuum sealing precedes labeling, link seal integrity results to label IDs to contain defects by lot. Steps: configure OCR/OCR-B; calibrate lighting; challenge with 25 label variants; log to historian. Risk boundary: quarantine if OCR mismatch > 0.4% in any hour. Governance: monthly review with Regulatory to align claims per region.
IQ/OQ/PQ Sequencing
Run IQ on printers/vision, OQ on 30 worst-case SKUs, PQ on three consecutive lots. Cite 21 CFR Part 11 for e-sign and GS1 for SSCC. Steps: approve URS, execute OQ, lock recipes, archive PQ. Risk: stop if PQ FPY < 98.5%.
Using RACI Matrices for Clear Accountability
Clear roles reduce MTTR and stabilize changeovers. A site that published a RACI for cobot–sealer ownership moved MTTR from 72 to 49 min across two quarters while holding OEE at 80%. Reference ISO 9001 for responsibility and authority, and IEC 62443-3-3 for cybersecurity roles. Steps: define who owns centerline, tooling, PLC logic, and e-records; train against e-SOPs; audit monthly. Risk boundary: trigger management review if overdue CAPAs > 3. Governance: attach RACI to MOC and training records.
Procurement queries like how much is a vacuum sealer belong in RACI under CapEx justification, with Ops validating kWh/pack and QA validating seal tests (ASTM F88). Steps: set TCO model; include spare kits; benchmark MTBF/MTTR; validate with SAT. Risk boundary: re-bid if payback > 24 months under base-case volumes. Governance: Finance owns TCO; Engineering owns technical scoring.
Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance
Preventive at 250 h intervals; predictive where torque or vacuum trends drift 2σ. Cite ISO 17359 for condition monitoring and ISO 13849-1 for safety validation. Steps: trend, alert, inspect, close CMMS. Risk: escalate if three alerts ignored in a week.
Governance Frameworks for Global Packaging Operations
A layered framework keeps cobots, ASFL controls, and serialization aligned across sites. Use ISA-95 for integration, ISO 27001 and IEC 62443 for security, and GS1 for data exchange. A three-plant rollout showed payback in 14–18 months at 2 shifts/day, with kWh/pack variance within ±0.02. Steps: standardize URS; enforce centerline library; validate with IQ/OQ/PQ; conduct annual cybersecurity audits. Risk boundary: suspend remote access if failed IEC 62443 audit items > 2. Governance: global CoE curates standards and approves deviations.
For artisan SKUs and a for jars vacuum sealer stream, define a lighter control set while preserving record integrity. Steps: lock manual checks, barcode lids, document torque checks, verify seals by AQL. Risk boundary: increase sampling to AQL 0.65 if defect spikes > 600 ppm. Governance: publish a variance guide and tie it to training plans.
Economics vs Compliance Balance
Model payback versus compliance workload. Include CapEx, kWh/pack, labor FTE, and validation costs. Cite ISO 50001 and Annex 11. Steps: run sensitivity, document assumptions, confirm with FAT/SAT, approve via QBR. Risk: re-scope if payback > 20% off baseline.
- References (Smart Sensors): ISO 13849-1; IEC 61131-3; ISO 2859-1; GS1 SSCC.
- References (Smart Factories): ISA-95; ISO 50001; IEC 60204-1; ISO 22400.
- References (Artwork): 21 CFR Part 11; Annex 11; ISO/IEC 15415; GS1 GTIN/GLN.
- References (RACI): ISO 9001; IEC 62443-3-3; ASTM F88; ISO 17359.
- References (Governance): ISO 27001; IEC 62443; GS1; 2006/42/EC.
Bottom line: cobots plus ASFL deliver stable OEE, documented safety (PL d), and controlled energy per pack when instrumented, governed, and validated with discipline.