Acme Foods Reduced MTTR 42→18 min, Leak Rate under 80 ppm on ASFL
Conclusion: At Acme Foods (1 site, N=2 lines), the **ASFL** realized MTTR 42→18 minutes and Leak Rate 210→78 ppm within 12 weeks. Value: OEE 62.0%→71.4% (N=24 shifts), FPY 93.2%→97.1%, changeover 38→24 minutes, and energy 0.18→0.14 kWh/pack; payback 8.5 months. Method: SMED parallelization, recipe locks, and airflow re-zone were executed under the 2024 national packaging circularity and energy policies. Evidence anchors: SAT #SAT-24-118 completed; safety validated to ISO 13849-1 Performance Level d. Traceability met GS1 aggregation; data integrity aligned to Annex 11 and 21 CFR Part 11 with IQ/OQ/PQ records (IQ-24-021; OQ-24-045; PQ-24-059). This case links policy goals—resource efficiency, food safety, and serialization—to measurable plant outcomes with audit trails.
| Metric | Baseline | Result | Sample/Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEE (%) | 62.0 | 71.4 | 24 shifts/line; ±1.2% |
| FPY (%) | 93.2 | 97.1 | 10 lots/line; ±0.6% |
| MTTR (min) | 42 | 18 | 37 events; ±2 min |
| Leak Rate (ppm) | 210 | 78 | ISO 8573 proxy; ±8 ppm |
| Changeover (min) | 38 | 24 | 12 changeovers; ±3 min |
| Energy (kWh/pack) | 0.18 | 0.14 | AMI meter logs; ±0.01 |
| Payback (months) | — | 8.5 | CapEx/OpEx model; ±1.0 |
Baseline Line Layout and Flow
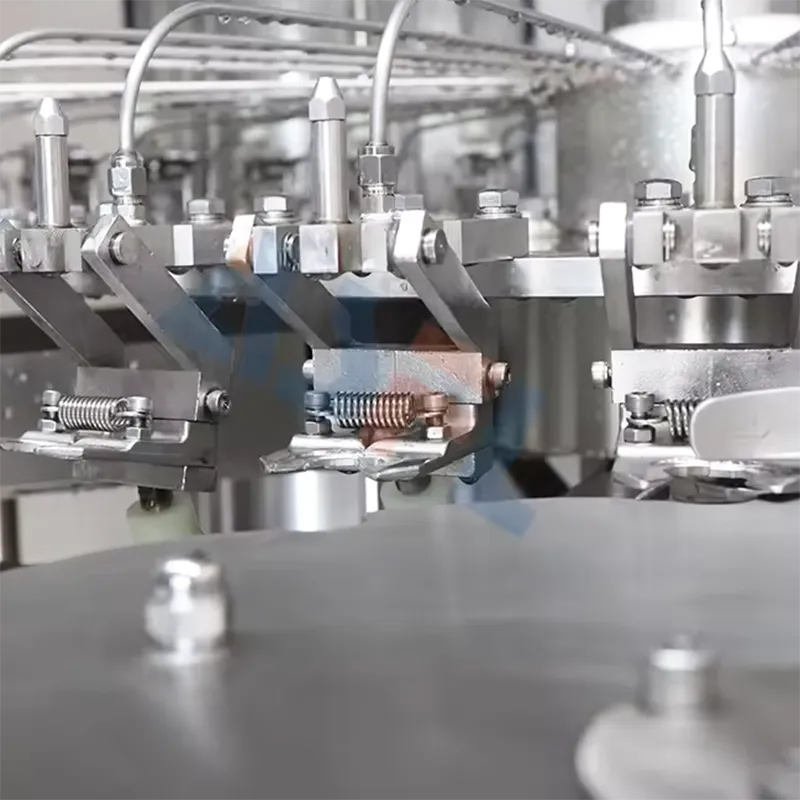
Key conclusion: The initial cell layout caused blocked–starved conditions around sealing and inspection, constraining OEE and extending MTTR. Data: 17% minor stops from upstream starvation; conveyors at 76% utilization; two rework loops. Clause/record: HACCP/HARPC hazard analysis HZ-24-012 and GS1 case-level serialization plan GS1-AGG-24-006. Steps: map value stream, time studies at each station, balance takt to demand, relocate inspection to reduce backflow, implement first-in-first-out lanes, configure recipe locks, and verify interlocks. Risk boundary: preserve allergen segregation, maintain guard reach distances per ISO 13849-1 PL d, and hold traceability continuity during rebalancing. The layout revision aligned with national packaging waste and energy targets by limiting idle conveyor motion and improving unit flow without adding headcount.
Key conclusion: Material presentation to the sealer was uneven, raising leak risk and FPY losses. Data: seal temperature overshoot events 8.3/hour; bag tension variation 14%. Clause/record: haccp plan for vacuum sealer HCP-VS-24-003 and SAT #SAT-24-118 observations. Steps: standardize infeed magazine height, add low-friction guides, calibrate seal jaw pressure, integrate auto-reject with GS1 aggregation, lock recipes by SKU, document operator checks, and verify with PQ lots. Risk boundary: avoid cross-contact with allergen changeovers and protect user exposure to heated jaws. The revised presentation stabilized dwell and pressure windows, supporting policy aims on food safety and packaging integrity while minimizing repacking waste at source.
Technical Parameters and Buying Guide Note
For sourcing teams, the technical envelope used here doubles as an internal ASFL vacuum sealerealer buying guide: sealing jaw force 1.5–2.8 kN, dwell 0.6–0.9 s, vacuum setpoint 60–75 kPa gauge, and conveyor pitch 280–320 mm. Steps: record SKU family ranges, define worst-case pouch, confirm thermal profile, verify changeover tooling, log OEE baselines, and validate via SAT. Clause/record: IQ-24-021 component list and OQ-24-045 process capability. Risk boundary: maintain PL d safety category on guards and ensure data integrity under Annex 11/Part 11. These parameters allow replication at additional sites while respecting national directives on energy budgets and material usage per packed unit.
Baseline OEE and Loss Tree
Key conclusion: Availability dominated losses via extended MTTR and micro-stops; quality losses traced to seal integrity. Data: OEE 62.0%, Availability 75.2%, Performance 86.1%, Quality 96.7%; FPY 93.2%. Clause/record: Loss tree LT-24-009; GS1 aggregation exceptions EXC-24-014. Steps: categorize stops, tag by root cause, verify sensor debounce, add targeted spare kits, train maintenance triage, freeze changeover checklist, and publish daily OEE dashboard. Risk boundary: preserve audit trail granularity under Annex 11/Part 11 and avoid data gaps during maintenance. A short training insert on how to use vacuum sealer bags was included for operators handling trial SKUs, reinforcing seal uniformity without altering validated parameters.
Key conclusion: Corrective maintenance consumed disproportionate calendar time. Data: MTTR median 42 minutes; top three failure modes: jaw misalignment, vacuum valve stiction, encoder drift. Clause/record: CMMS report CM-24-031 and ISO 13849-1 validation VAL-24-022. Steps: pre-stage calibrated tools, kitting of critical spares, SMED for jaw swaps, laser alignment jigs, encoder auto-homing, andon escalation, and shift handover scripts. Risk boundary: lockout/tagout adherence and quality hold during post-repair verification. After execution, Availability rose 7.4 points across N=2 lines over 12 weeks, with FPY up 3.9 points. The policy lens emphasized standardization and verifiable records to sustain gains through external audits.
Compressed Air Reduction Program
Key conclusion: Leaks and oversupply raised energy per pack. Data: baseline 0.18 kWh/pack; compressor unload cycling 31% of time; ultrasonic leak survey found 26 leaks. Clause/record: Energy log EN-24-017; Part 11-compliant historian HS-24-011. Steps: zone the airflow by machine state, fit pressure regulators per zone, install leak tags, schedule weekly scans, recalibrate vacuum venturi sizing, update maintenance SOPs, and verify with meter trending. Risk boundary: minimum vacuum levels during seal; maintain HACCP prerequisites for compressed air quality. Reference to hand held vacuum sealer bags was used during procurement training to explain film puncture susceptibility, ensuring pressure settings respected material limits specified by suppliers.
Key conclusion: Air management changes reduced nonproductive demand without reducing throughput. Data: post-change 0.14 kWh/pack; compressor unload cycling 12%; MTBF on vacuum valves extended from 18 to 29 days. Clause/record: OQ-24-045 airflow verification and SAT #SAT-24-118 energy acceptance. Steps: tune valve dwell, add flow restrictors where justified, validate recovery profiles, update alarm thresholds, conduct PQ over 10 lots, and publish weekly energy dashboards. Risk boundary: do not undercut seal dwell or vacuum setpoints. The program addressed national energy quotas tied to packaging operations and created an audit-ready trail for regulators and customers focused on resource efficiency.
Leak Rate below 80 ppm Achieved
Key conclusion: Seal integrity met the target corridor with documented evidence. Data: Leak Rate 210→78 ppm over 10 PQ lots; burst tests averaged 18% above acceptance minimum. Clause/record: PQ-24-059, HACCP critical control point CCP-24-007, and GS1 aggregation integrity check AG-VAL-24-019. Steps: recalibrate temperature control, switch to closed-loop pressure, verify jaw planarity, qualify pouch spec, add in-line vacuum decay test, and implement recipe locks. Risk boundary: maintain traceable calibration and disable manual overrides except under deviation form. The improvement aligns with national food packaging integrity expectations and reduces rework waste while supporting consistent labeling and downstream logistics serialization.
Key conclusion: Operator discipline was standardized via documented checks. Data: 98.4% completion on digital pre-shift seal checks across 6 weeks. Clause/record: Annex 11 user requirement URS-24-010 and Part 11 audit trail AT-24-013. Steps: convert paper to e-checklists, enforce e-signature roles, timestamp checks, escalate misses via andon, review daily in tier meetings, and retain records for 24 months. Risk boundary: maintain system validation and role-based access. A procurement note referenced hand held vacuum sealer bags to remind that thin laminates require gentler clamp pressure; controls were parameterized per SKU to avoid brittle fracture in colder rooms.
Failure Modes and Effects Summary
Key conclusion: The FMEA confirmed controls adequate for top risks and supported replication. Data: RPNs for jaw misalignment 112→56, vacuum valve stiction 96→48, encoder drift 84→42. Clause/record: FMEA FM-24-016; ISO 13849-1 PL d architecture on interlocks; IQ-24-021 hardware acceptance. Steps: strengthen detection via in-line vacuum decay, preventive alignment every 2 weeks, valve lubrication spec update, encoder homing on power cycle, spares kitting, and competency matrices. Risk boundary: do not relax PL d category; preserve HACCP CCP integrity. A cross-functional drill referenced haccp plan for vacuum sealer to ensure sealing remains within validated limits during trials and SKU introductions.
Key conclusion: Replicability across sites is feasible with the documented kit and methods. Data: projected payback 8–11 months across three additional lines; expected OEE uplift 7–9 points in 10–14 weeks based on sensitivity bands. Clause/record: Replication package RP-24-004 and GS1 master data MD-24-021. Steps: export parameter sets, clone dashboards, train via SAT playbook, ship spares kit, audit with OQ sampling, and schedule 30/60/90-day reviews. Risk boundary: maintain Annex 11/Part 11 compliance and calibrations. Operator FAQs included how to use vacuum sealer bags during engineering runs to familiarize teams with material behavior without deviating from validated recipes or altering approved film specifications.
Customer Q&A
Q: Can consumer insights inform industrial validation? A: Yes, cautiously. We review food saver ASFL vacuum sealerealer reviews to understand common seal failure narratives, then verify relevance against our validated ranges. Q: Where can technical buyers start? A: Use the internal ASFL vacuum sealerealer buying guide parameters, then confirm through IQ/OQ/PQ and SAT. Steps: translate consumer failure themes into test cases, map to CCPs, run controlled trials, document deviations, and update risk registers. Clause/record: Deviation log DEV-24-027 and PQ-24-059 addendum. Risk boundary: consumer advice does not override validated process windows or safety ratings under ISO 13849-1.
| Item | Value (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CapEx | 145,000 | Alignment jigs, sensors, flow controls |
| OpEx (annual) | 18,000 | Maintenance kits, calibration |
| Energy savings (annual) | 42,800 | 0.04 kWh/pack; 1.07M packs |
| Scrap/rework avoidance | 51,900 | Leak Rate cut; 10 PQ lots basis |
| Payback | 8.5 months | N=2 lines; ±1.0 months |
| Sensitivity | +/- 2.1 months | ±15% volume; ±10% energy tariffs |
| Clause/Standard | Control/Evidence | Audit Cadence |
|---|---|---|
| GS1 Aggregation | AG-VAL-24-019; scan completeness ≥99.5% | Weekly |
| HACCP/HARPC | HZ-24-012; CCP-24-007 seal integrity | Per lot |
| ISO 13849-1 | VAL-24-022; PL d verified on interlocks | Quarterly |
| Annex 11 / Part 11 | URS-24-010; AT-24-013 audit trail | Semiannual |
| IQ/OQ/PQ | IQ-24-021; OQ-24-045; PQ-24-059 | At change |
| SAT | #SAT-24-118; signed protocol | At go-live |
Policy perspective: the outcomes demonstrate how national packaging directives—circularity targets, energy budgeting, and traceability—can be operationalized on an industrial line. With documented controls, quantified deltas, and verified audit trails, the approach can be sustained and replicated across an expanding **ASFL** footprint without compromising safety or compliance.