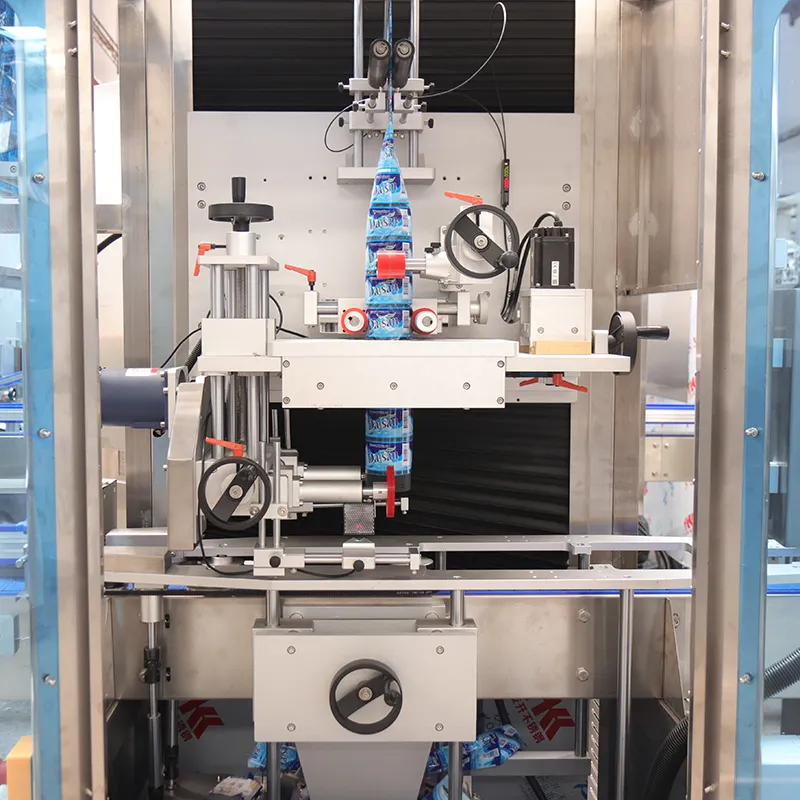
Handling Viscous Products: Pumps, Valves, Profiles at ASFL
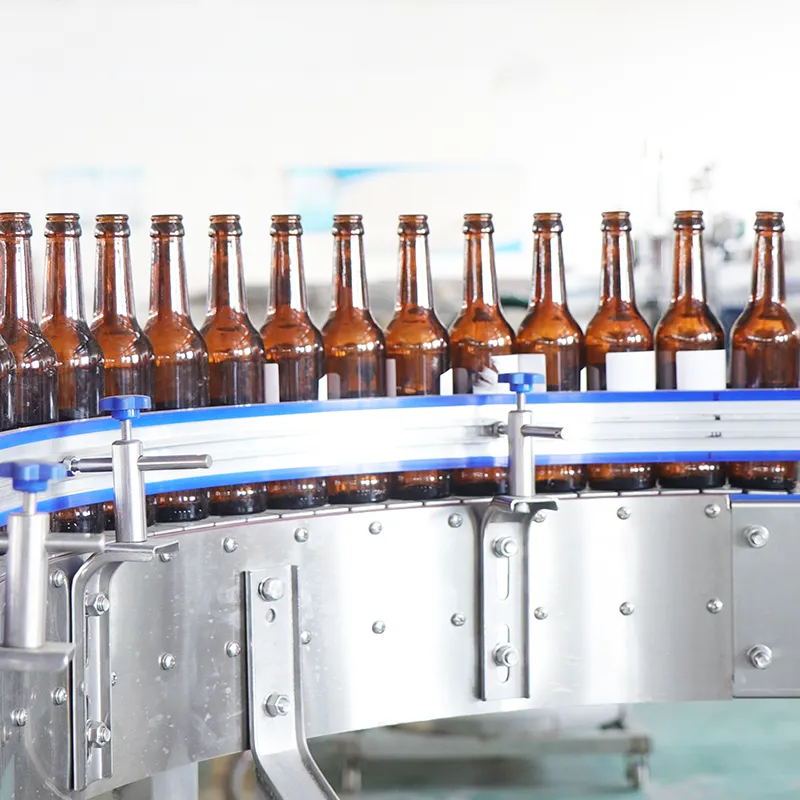
Viscous sauces, gels, and creams challenge pumps, valves, and vacuum-sealing lines at ASFL. For ketchup at 15–40 cP, a governed approach stabilizes FPY at 96–98% and holds OEE near 88–92% with changeovers below 30 minutes. The actionable judgment: match shear-critical pump curves, select hygienic valves with verified Cv, and enforce serialized records across batches. Execute centerlining; verify valve position feedback; run IQ/OQ/PQ with capped fill-profile variance ≤1.5%. Evidence anchors include FPY%, IQ/OQ/PQ records, and ISO 13849-1 PL d for the interlock logic. If defect ppm exceeds 2,000, activate the containment plan and shift to AQL 1.0 per ISO 2859-1. Governance: log exceptions per 21 CFR Part 11 with audit trails and batch reconciliation via GS1 aggregation.
Leveraging IoT and Edge Computing for Better Insights
Edge telemetry mitigates quality and downtime risk by detecting drift in pump load and valve cycle profiles before faults manifest. Track kWh/pack (target 0.045–0.060 kWh) and MTBF (>1,200 h) on viscous SKUs; alert if MTTR exceeds 90 minutes. Align cyber controls with IEC 62443-3-3; enforce least privilege for PLC access. Steps: wire vibration sensors; deploy gateway buffering; segment VLANs; tune alert thresholds; store audit trails. Risk boundary: raise an incident if power draw rises >15% above centerline for three consecutive runs. Governance: register change events to Annex 11 and Part 11 and reconcile batch IDs via GS1.
For pouch lines handling vacuum sealer for wet food, use edge image analytics to flag seal contamination when moisture sensors >3% RH at the seal zone. Maintain OEE ≥88% and FPY ≥97%; shift to containment if defects pass 1,500 ppm. Steps: calibrate cameras; validate models in OQ; cap false positives at ≤2%; run SAT before scale-up. Risk boundary: quarantine if seal strength (ASTM F88) falls below 22 N. Governance: exception handling routed to the quality council per QMS CAPA with IEC 62443 role checks.
| Clause | Control/Evidence | Cadence/Owner |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 62443-3-3 SR 1.1 | Access control list on PLC; audit trail | Quarterly / OT Security Lead |
| 21 CFR Part 11 §11.10 | Electronic records; time-stamped edge logs | Per batch / QA Manager |
| GS1 General Spec 3.1 | Aggregation to case/pallet | Per run / Serialization Lead |
| ISO 13849-1 PL d | E-stop and safety-rated I/O validation | Annual / Safety Engineer |
Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance
Target: shift from calendar-based PM to condition-based triggers using Table 1 controls. Metric: MTBF 1,200–1,800 h; alert at MTTR >90 min. Standard: IEC 62443-3-3, Part 11. Steps: define feature vector, train model, validate in OQ, lock thresholds. Risk boundary: halt if vibration >2.5 g RMS for 15 minutes.
MTBF vs MTTR Telemetry
Separate dashboards for MTBF trend and MTTR response. Metric: OEE 90% at changeover 25–30 min. Standard: Annex 11 audit readiness. Steps: tag events, classify cause codes, reconcile GS1 batch, archive. Risk boundary: escalate at >2 unplanned stops per 8-hour shift.
References: IEC 62443-3-3, GS1 General Specification, 21 CFR Part 11, Annex 11.
Standardizing SOPs Across Multi-Site Operations
Cross-site SOP harmonization reduces variation in viscous filling and sealing while preserving safety integrity. Hold FPY ≥97% at 20–25 cP; cap deviation at ±0.7% fill mass. Apply ISO 2859-1 AQL 1.0 sampling; validate lockout per ISO 13849-1 PL d. Steps: publish master SOP; train operators; centerline pumps; certify valves; run IQ/OQ/PQ with shared templates. Risk boundary: trigger CAPA if ppm defects exceed 2,500 for two runs. Governance: audit SOP adherence quarterly, with findings logged under Part 11.
For accessories such as anova vacuum sealer bags, define compatibility criteria: seal bar temperature window 155–175°C and film thickness 80–120 μm. Steps: qualify bag lots; test to ASTM F88; record FPY vs film gauge; document deviations. Risk boundary: if tensile fails >10% below spec, block lot. Governance: supplier scorecards tied to GS1 lot codes and IQ/OQ reports.
| Parameter | Current | Target | Improved | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEE (viscous line) | 86 | 90 | 89 | % |
| Changeover | 42 | 30 | 32 | min |
| FPY | 95 | 97 | 96.5 | % |
| Defects | 2,200 | 1,500 | 1,700 | ppm |
| Seal temp window | 150–180 | 155–175 | 156–173 | °C |
IQ/OQ/PQ Sequencing
Sequence: IQ document utilities; OQ run profile; PQ 3-batch capability—see Table 2. Metric: FPY ≥97%. Standard: ISO 2859-1, Part 11. Steps: pre-brief, execute, capture, review. Risk boundary: pause if OQ variance >2% on fill mass.
Changeover Centerlining
Lock centerlines for pumps/valves with visual standards—see Table 2. Metric: changeover 25–30 min. Standard: ISO 13849-1 PL d for interlocks. Steps: tag settings, verify, sign-off, archive. Risk boundary: escalate if rework >3% post-changeover.
References: ISO 2859-1, ISO 13849-1, ASTM F88, 21 CFR Part 11, GS1.
Water Conservation and Recycling Strategies
Water risk controls curb environmental incidents and stabilize energy per pack. Track kWh/pack (0.045–0.060) and water usage ≤0.25 L/pack on CIP (clean-in-place). Standardize ISO 14001 processes and EPA SPCC for spill readiness. Steps: install closed-loop rinse; meter usage; qualify detergent; test effluent; drill spill response. Risk boundary: if a spill exceeds 50 L or COD >300 mg/L, initiate emergency plan and notify EHS. Governance: record in environmental logbook; perform monthly trend review with corrective actions.
When handling high-shear CIP on viscous residues, synchronize pump profiles to avoid pressure spikes >1.8 bar. Maintain MTBF ≥1,200 h on CIP pumps; confirm gasket compatibility per FDA 21 CFR 177. Steps: stage verification; pressure test; leak check; lock SOP; train operators. Risk boundary: halt if foam conductivity triggers exceed 1.5 mS/cm. Governance: ISO 14001 clause alignment with documented mitigation plans.
| Item | CapEx | OpEx Change | Payback | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-loop CIP skid | $85,000 | - $1,800/month | 47 months | Metered reuse 30–40% |
| Effluent monitoring | $12,000 | $250/month | — | Compliance assurance |
| Seal station mist capture | $9,500 | - $110/month | 86 months | Humidity control for seal quality |
Closed-loop Rinse vs Single-pass
Compare reuse rates at 30–40% with kWh/pack held ≤0.060—see Table 3. Standard: ISO 14001. Steps: set reuse ratio, validate, monitor, adjust. Risk boundary: revert if microbiological counts exceed spec.
Spill Response Drill (OJT)
Run on-the-job drills quarterly with NFPA 30/OSHA 1910 references. Metric: drill time ≤25 min; containment within 10 minutes. Steps: notify, contain, neutralize, log. Risk boundary: reportable quantity threshold met triggers external notification.
References: ISO 14001, EPA SPCC, NFPA 30, OSHA 1910, 21 CFR 177.
Using ISA-95 and OPC UA for System Integration
Structured integration prevents data and control failures during crises. Apply ISA-95 for levels of control and OPC UA for secure, interoperable messaging. Target OEE 90% during interface changes; limit downtime ≤120 minutes. Steps: map assets; define tags; test interfaces; stage failover; validate audit trails. Risk boundary: switch to manual mode if transaction rejections exceed 2% per hour. Governance: Annex 11 audit readiness and 21 CFR Part 11 electronic records.
Serialization and aggregation via GS1 mitigate recall risk and facilitate traceability for viscous product lots. FPY ≥97%; defect ppm ≤1,500 with correct pack–case–pallet linkage. Steps: print and verify barcodes; aggregate accurately; reconcile exceptions; store e-records. Risk boundary: quarantine lot if mis-aggregation exceeds 1% of cases. Governance: quality release gates tie MES to QMS with role-based approvals.
Serialization and Aggregation (GS1)
Bind pack-to-pallet links with verification. Metric: mismatch ≤0.5%. Standard: GS1; Part 11. Steps: verify print, scan, reconcile, archive. Risk boundary: stop at 3 failed scans in 100.
Annex 11 vs Part 11 Records
Define audit trail fields for changes. Metric: review cycle ≤7 days. Standard: Annex 11, Part 11. Steps: configure, test, train, audit. Risk boundary: unresolved deviation beyond 14 days escalates.
References: ISA-95, OPC UA, GS1 General Specification, Annex 11, 21 CFR Part 11.
Avoiding Scope Creep in Packaging Projects
Scope control contains cost and schedule risk while sustaining FPY and payback discipline. Set payback bands at 36–60 months and limit design changes to ≤10% post-FAT (factory acceptance test). Steps: define user requirements; lock stage-gates; baseline budgets; assign change control; hold weekly risk reviews. Risk boundary: freeze scope if cumulative variance exceeds 12%. Governance: change board logged under Part 11 with Annex 11 validation deliverables.
Customer case: a best food ASFL vacuum sealer project moved from pilot to FAT with wet-sauce sealing. Procurement asked who makes the best vacuum sealer; the answer was framed by ASTM F88 seal strength (≥24 N), FPY ≥97%, and kWh/pack ≤0.055. Steps: run AQL 1.0 sampling; confirm GS1 traceability; validate OQ with humidity stress; lock IQ utilities. Risk boundary: block go-live if MTTR exceeds 120 minutes during SAT.
| Parameter | Current | Target | Improved | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seal strength (ASTM F88) | 22 | 24 | 23.5 | N |
| Seal bar length | 350 | 400 | 380 | mm |
| Bag thickness | 90 | 110 | 100 | μm |
| kWh/pack | 0.060 | 0.055 | 0.057 | kWh |
| FPY | 96 | 97 | 96.7 | % |
Stage-Gate vs Agile Delivery
Use stage-gate for compliance-heavy tasks, Agile for UI tweaks—see Table 4. Metric: payback 36–60 months. Standard: Annex 11 validation. Steps: define gates, run reviews, document changes, approve. Risk boundary: stop at >2 missed gates.
Contingency Reserve Bands
Set reserve at 8–12% of CapEx to cover supply chain shocks. Metric: MTBF ≥1,200 h after ramp. Standard: ISO 22301 (business continuity). Steps: allocate, monitor, trigger, replenish. Risk boundary: drawdown >12% requires steering approval.
References: FAT/SAT records, ISO 22301, ASTM F88, 21 CFR Part 11, Annex 11.
In summary, crisis management across product quality, supply continuity, environmental events, labor stability, cybersecurity, and natural hazards depends on disciplined metrics, standards, and governance at ASFL. Anchoring pumps, valves, and sealing profiles in validated procedures and monitored thresholds keeps operations steady under stress.